基础算法与数据结构(八) 最小生成树与并查集
什么是最小生成树?
在图G上,如果一个强连通图上的每条边上都有一个权重值,权重值可以是一个负数或零。那么一定可以找到一个无环边子集能够把这个图上的所有的点能够连接起来。
这个五环边子集的权重和如果是所有子集中最小的,那么这个边子集构成的一定是一棵树,所以把它称之为 最小生成树。
同样的,最小生成树不一定是唯一的。
最小生成树的性质
- 最小生成树的边数目一定是V-1,V是图的顶点数。
如何产生一棵最小生成树?
最小生成树有两种算法可以用来生成,Kruskal算法和Prim算法。
这两种算法都是一种贪心算法,每一步都得到当前一部的最优选择,虽然贪心算法不能够保证全局最优,但是在最小生成树的算法中可以证明得到一棵全局最优的最小生成树。(在算法导论中可以用“安全边”的概念进行证明,由于
需要一些概念,避免篇幅过长,此处从略,可详见算法导论中文版P363-364)
这里给出两种算法都通用的一个求出的思想伪代码,也是写在《算法导论》中的伪代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
GENERIC-MST(G,w)
1 A = ∅
2 while A does not form a spanning tree
3 find an edge(u,v) that is safe for A
4 A = A ∪ {(u,v)}
5 return A
两种算法的区别就是找到第3行中所写的安全边方法的区别。
并查集(Union-Find)
在讲述这两个算法之前,先讲述一个数据结构用来高效判断两点是否属于同一集。这个数据结构就是并查集。
并查集能够完成的事情就是得到一个并的指令或者查询的指令,从要完成的功能上来看也是非常容易的。
并查集是个高效的数据结构,不过可能会产生不高效的情况下,所以多加了一部加权的步骤,把小树的根节点连接到大树的根节点上。
并查集的算法代码给出,此处为JAVA代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public class WeightedQuickUnionUF{
private int[] id; //父节点索引
private int[] sz;
private int count; //连通分量的数量
public WeightedQuickUnionUF(int n){
count = n;
id = new int[n];
//初始化时,所有结点的父节点均为自己
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) id[i] = i;
sz = new int[n];
//根节点对应的树的高度为1
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) sz[i] = 1;
}
public int getCount(){
return count;
}
public boolean isConneted(int p,int q){
//找到最后的根节点,如果两个根节点是相同的,那么就属于同一个集合
return find(p) == find(q);
}
public int find(int p){
//由于初始化的原因,只有当父节点是自己的时候,就是最后的根节点
while(p != id[p]) p = id[p];
return p;
}
//返回是否合并
public bool union(int p,int q){
int i = find(p);
int j = find(q);
//如果已经属于了同一个根节点,那么不需要合并了
if( i == j ) return false;
//小的树合并到大的树上
if(sz[i] < sz[j]){
id[i] = j;
sz[j] += sz[i];
}else{
id[j] = i;
sz[i] += sz[j];
}
count--; //连通分量减少
return true;
}
}
以上就是并查集的JAVA实现代码,其实其他语言的实现方法都差不多。
不过上面的这个算法并不是最佳的,最好的算法是 路径压缩的加权并查集算法 才是最优的,均摊成本无限接近O(1)。
上面的这个加权算法,union和find的时间复杂度都是lgN。
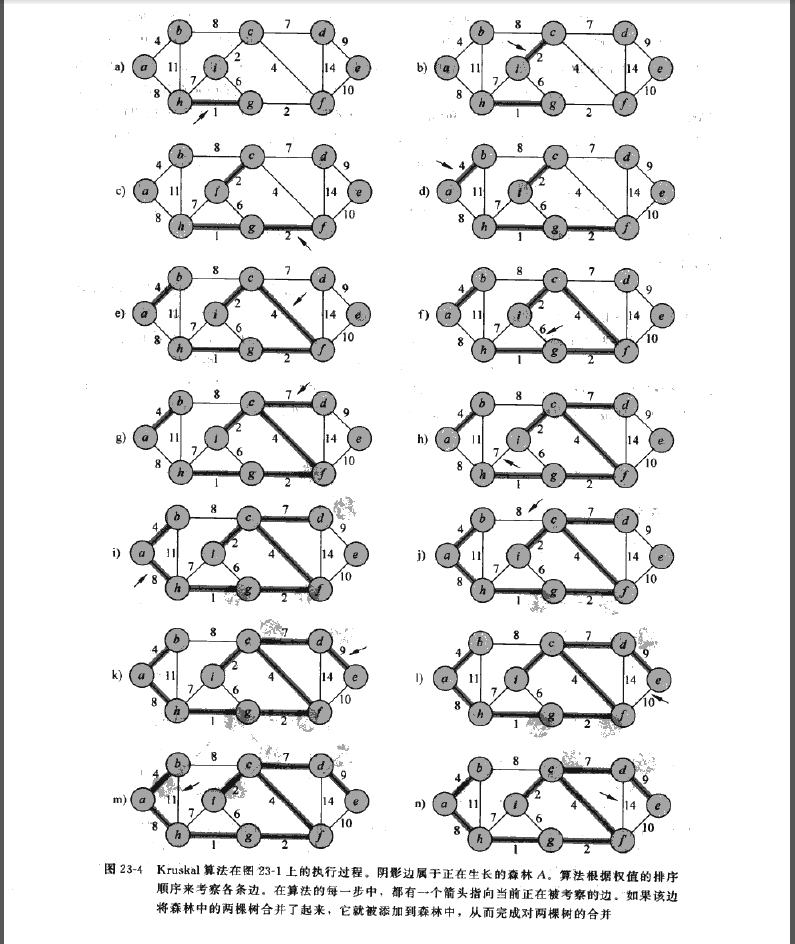
Kruskal算法
这个算法找到安全边的方法是,每次在所有的边中找到权值最小的,并且连接的两个顶点不在同一个集合中,那么就将这个边加入生成树中,并且union这两点。
Kruskal算法的时间复杂度为O(ElgV) E为边的数目,V为顶点的数目。
因为需要对边进行排序,所以在这个中需要新增加一个边的集合,容易进行排序。
先上代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
struct edge{
//u,v为边的起点终点,w为权值
int u;
int v;
int w;
}
vector<edge> e; //边的集合
vector<edge> tree; //答案的最小生成树
bool cmp(edge p,edge q){
return p.w < q.w;
}
WeightedQuickUnionUF UF;
void Kruskal(){
UF = new WeightedQuickUnionUF(e.size());
sort(e.begin(),e.end(),cmp);
ans = 0; //权值的答案
for(int i = 0; i <= e.size(); i++){
//合并了,需要加入树,加上权值。
if(UF.union(e[i].u,e[i].v)){
ans += e[i].w;
tree.push_back(e[i]);
}
}
}
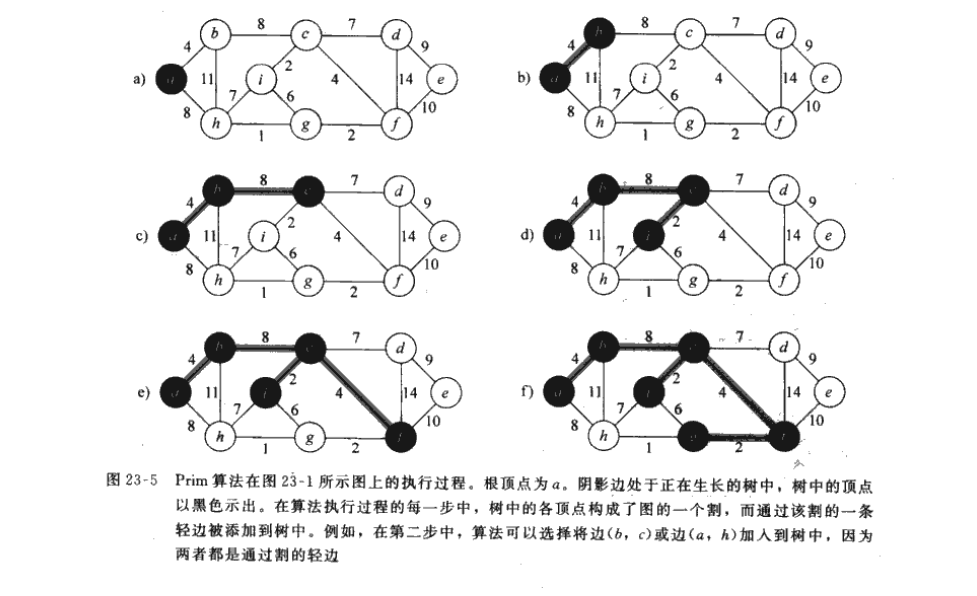
Prim算法
Prim算法找安全边的想法主要是,从一个根节点开始,找这个根节点连接的边中最小权值的边加入最小生成树,一直到这棵树找到所有的节点。
在prim算法中,需要一种优先队列的数据结构,这种数据结构在C++中有内置的STL实现,这里省略了具体讲解,总而言之优先队列会根据某种给定的排序算法,每次取出的值都是最大的或者最小的。
Prim算法的实现具体代码如下:参考了geeksforgeeks网站,所以注释都是英文(MST - 最小生成树)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
// STL implementation of Prim's algorithm for MST
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
# define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
// iPair ==> Integer Pair
typedef pair<int, int> iPair;
// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex
// and weight pair for every edge
list< pair<int, int> > *adj;
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w);
// Print MST using Prim's algorithm
void primMST();
};
// Allocates memory for adjacency list
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<iPair> [V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v, w));
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u, w));
}
// Prints shortest paths from src to all other vertices
void Graph::primMST()
{
// Create a priority queue to store vertices that
// are being preinMST. This is weird syntax in C++.
// Refer below link for details of this syntax
// http://geeksquiz.com/implement-min-heap-using-stl/
priority_queue< iPair, vector <iPair> , greater<iPair> > pq;
int src = 0; // Taking vertex 0 as source
// Create a vector for keys and initialize all
// keys as infinite (INF)
vector<int> key(V, INF);
// To store parent array which in turn store MST
vector<int> parent(V, -1);
// To keep track of vertices included in MST
vector<bool> inMST(V, false);
// Insert source itself in priority queue and initialize
// its key as 0.
pq.push(make_pair(0, src));
key[src] = 0;
/* Looping till priority queue becomes empty */
while (!pq.empty())
{
// The first vertex in pair is the minimum key
// vertex, extract it from priority queue.
// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
// has to be done this way to keep the vertices
// sorted key (key must be first item
// in pair)
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
inMST[u] = true; // Include vertex in MST
// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex
list< pair<int, int> >::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
{
// Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
// of u.
int v = (*i).first;
int weight = (*i).second;
// If v is not in MST and weight of (u,v) is smaller
// than current key of v
if (inMST[v] == false && key[v] > weight)
{
// Updating key of v
key[v] = weight;
pq.push(make_pair(key[v], v));
parent[v] = u;
}
}
}
// Print edges of MST using parent array
for (int i = 1; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d - %d\n", parent[i], i);
}
图示: 摘自算法导论
例题
暂缺。